The particle size distribution of a powder can be determined in two different ways: by means of a sieve analysis and by means of a laser diffraction analysis.
Particle size distribution
With a sieve analysis the original sample is sieved into several fractions by means of a sieve tower. The partitioning is determined by weighing the different fractions. An example of particle size distribution made by a sieve analysis is presented in the table below:
| fraction | weight percentage |
|---|---|
| < 63 µm | 56.00 % |
| 63 µm < x < 125 µm | 40.35 % |
| 125 µm < x < 200 µm | 3.20 % |
| 200 µm < x < 500 µm | 0.25% |
| > 500 µm | 0.20% |
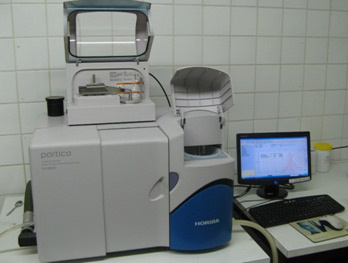
A second possibility determining the particle size distribution is by means of a laser diffraction analysis. The particle size distribution can be determined with the laser diffraction apparatus HORIBA LA 950 V2 according to the standard ISO 13320. This apparatus has a liquid and a dry dispersion unit and provides a wide dynamic range from 0.01 µm to 3000 µm.